Boiled eggs are a valuable source of protein and vitamins. A good nutritional diet is the foundation for overall health, and the calorie content of one chicken egg depends on its weight. In this article, My Auris will reveal it to you!
How many calories in a boiled egg? A detailed analysis from experts
How many calories in 1 boiled egg? A large boiled chicken egg (approximately 50 grams) contains about 72-78 calories. According to data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), this figure is a reliable reference for dieting or sports nutrition.
This calorie level is not absolutely fixed. It can vary slightly depending on the size of the egg. However, boiled eggs are always a smart, low-calorie food choice compared to other cooking methods.
To understand the calorie content of chicken eggs more deeply, we need to separately analyze its two main components: the yolk and the white. The calorie distribution between these two parts differs significantly, and this is important information for those who want to optimize their meals.
- Egg white: Contains approximately 17 calories. Its main components are protein (albumin) and water. It is a high-quality protein source, almost fat-free.
- Egg yolk: Contains the majority of the calories, about 55 calories. This is where healthy fats, essential cholesterol, and important fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamin D, Vitamin A, and choline are concentrated. The yolk also contains lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants beneficial for eye health.

This distribution shows that if you are on a very strict diet, consuming only egg whites can help reduce calorie intake. However, eating the whole egg provides a complete protein source and many more essential nutrients.
How many calories in 2 boiled chicken eggs?
How many calories in 2 boiled chicken eggs? The answer is approximately 155 calories. This is the average for two large chicken eggs. Calories are units of energy that the body receives from food. Knowing the calorie content helps you control your weight and build a scientific eating plan.
However, this number is not fixed. The calorie content of chicken eggs depends on their weight. A larger egg will contain more calories. Below is a detailed food calorie table for your reference:
- Small chicken egg (approx. 38g): 54 calories
- Medium chicken egg (approx. 44g): 63 calories
- Large chicken egg (approx. 50g): 72 calories
- Extra-large chicken egg (approx. 56g): 80 calories
Thus, when you eat 2 eggs, the total calorie intake will range from 108 to 160 calories. The number 155 calories is often used as a common reference point. This calorie amount primarily comes from the egg yolk. The yolk contains most of the fats and vitamins. The egg white primarily contains protein and very few calories.
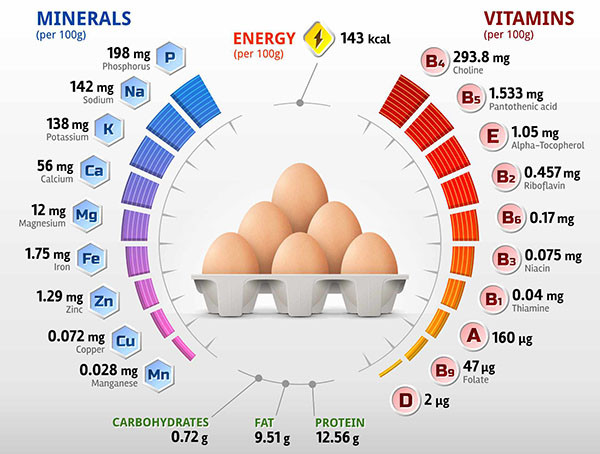
Nutritional Value of Boiled Chicken Eggs
Detailed nutritional composition table for one large boiled chicken egg (approx. 50g):
| Nutrient | Estimated Content | Main Role |
| Calories | ~77 kcal | Provides energy for the body. |
| Protein | ~6.3 g | Builds and repairs muscles and tissues. |
| Fat | ~5.3 g | Provides energy, supports vitamin absorption. |
| – Saturated Fat | ~1.6 g | |
| – Unsaturated Fat | ~2.7 g | Good for cardiovascular health. |
| Cholesterol | ~212 mg | Essential for hormone and cell production. |
| Vitamin D | ~44 IU (10% RDI) | Supports calcium absorption, boosts immunity. |
| Vitamin B12 | ~0.6 mcg (25% RDI) | Important for nerve function, blood formation. |
| Vitamin A | ~260 IU (5% RDI) | Good for vision and skin health. |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | ~0.3 mg (20% RDI) | Converts food into energy. |
| Choline | ~147 mg (27% RDI) | Extremely important for brain function. |
| Selenium | ~15.4 mcg (28% RDI) | Powerful antioxidant, protects cells. |
| Lutein and Zeaxanthin | ~252 mcg | Protects eyes from harmful blue light damage. |

Comparing calories in boiled chicken, duck, and quail eggs
Relative Nutritional Comparison Table (per 100g)
| Criterion | Chicken Egg (Approx. 2 large eggs) | Duck Egg (Approx. 1.5 eggs) | Quail Egg (Approx. 10-11 eggs) |
| Calories | ~155 kcal | ~185 kcal | ~158 kcal |
| Protein | ~13 g | ~13 g | ~13 g |
| Fat | ~11 g | ~14 g | ~11 g |
| Cholesterol | ~373 mg | ~619 mg | ~844 mg |
This table shows that when calculated for the same mass, duck eggs have significantly higher calorie and fat content. Quail eggs have similar calorie and protein content to chicken eggs but the highest cholesterol content. These are important factors to consider when developing a specific diet.
Amazing Health Benefits of Boiled Eggs
The protein in eggs is a complete protein source. This means it contains all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. One large chicken egg provides about 6 grams of high-quality protein. Protein plays a crucial role in building and repairing muscle tissue, especially important for those who exercise or want to maintain muscle mass as they age.
Eating boiled eggs for weight loss is a method successfully adopted by many. Thanks to their high protein content, boiled eggs help boost metabolism through an effect called the thermic effect of food. The body requires more energy to metabolize protein compared to other macronutrients. This helps you burn more calories.
Egg yolks are one of the richest dietary sources of Choline. Choline is an important nutrient, essential for building cell membranes and producing signaling molecules in the brain. A diet rich in Choline helps improve memory, mood, and cognitive function.
Egg yolks contain two powerful antioxidants: Lutein and Zeaxanthin. The content of lutein and zeaxanthin in egg yolks is very high. They accumulate in the retina of the eye and act as a filter for harmful blue light.
Many people are concerned about the cholesterol content in eggs. However, the latest studies from nutrition experts have shown that dietary cholesterol has little impact on blood cholesterol levels in most people. Instead, saturated and trans fats are the main culprits. Boiled eggs, when part of a balanced diet, can actually support cardiovascular health.
Eggs are a treasure trove of vitamins and minerals. They are one of the few natural foods containing Vitamin D, which is crucial for bone health and immune function. Eggs also provide a significant amount of Vitamin B12, necessary for nerve function and red blood cell formation. Furthermore, eggs contain Vitamin A, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Zinc.

How to Boil Chicken Eggs to Retain Nutrients
To achieve perfectly boiled eggs, you don’t need complex equipment. All you need is a pot, water, and eggs. The key lies in precise temperature and time control.
Step 1: Preparation
Choose eggs: Use fresh free-range or factory-farmed chicken eggs. Let the eggs sit at room temperature for about 15-20 minutes before boiling. This helps prevent the eggs from thermal shock when placed in water, minimizing shell cracks during boiling.
Prepare the pot: Choose a pot that is large enough to arrange the eggs in a single layer at the bottom. Do not stack the eggs on top of each other, as this will cause them to cook unevenly.
Step 2: Start Boiling
Place eggs in the pot: Gently place each egg at the bottom of the pot.
Add cold water: Pour cold water into the pot until it covers the eggs by about 2-3 cm. Starting with cold water is key for the eggs to cook evenly from the outside in. If you drop eggs into boiling water, the whites will cook too quickly while the yolks remain raw.
Step 3: Timing – The Deciding Factor
Bring to a boil: Place the pot on the stove and heat over high heat until the water comes to a rolling boil.
Turn off the heat and steep the eggs: As soon as the water boils, turn off the heat and cover the pot. Let the eggs steep in the hot water. This is the most crucial stage for the eggs to cook slowly with residual heat, helping the whites stay tender and the yolks reach the desired doneness without becoming dry or having a green ring.
Timing for steeping eggs in hot water (after turning off the heat):
4-5 minutes: Soft-boiled. The white is just set, the yolk is still liquid and runny. Ideal for those who like soft eggs and often serve them with toast.
6-7 minutes: Jammy yolk. This is the perfect doneness for a nutritious breakfast. The white is fully set, the yolk has a beautiful orange-yellow color, and the center is still gooey and moist, not dry. Protein and vitamin content are optimally preserved. This is an excellent choice for egg diets and sports nutrition.
9-10 minutes: Hard-boiled. Both the white and yolk are fully set but still retain their tenderness, not crumbly. Suitable for salads, sandwiches, or for those who prefer thoroughly cooked eggs.
Step 4: Proper Cooling
Remove eggs: Use a spoon to immediately remove the eggs from the hot water once the steeping time is over.
Ice bath: Immediately transfer the eggs to a bowl of cold ice water for about 5-10 minutes. This sudden cooling process has two effects: first, it stops the eggs from continuing to cook, and second, it causes the shell to contract, making them much easier to peel.
By following this process, you will not only have a delicious dish but also ensure good absorption of valuable nutrients. This method is easy to prepare, affordable, suitable for any meal plan, and a smart choice for your health.





