Are you experiencing knee pain? Does swelling and discomfort limit your movement? Knee effusion might be the cause. My Auris will share some folk remedies to help reduce pain and swelling from knee effusion right at home, supporting the treatment of knee conditions.
What is Knee Effusion?
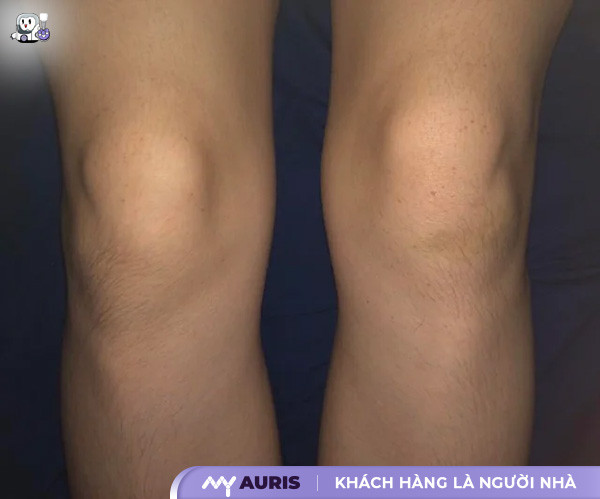
Knee effusion is a condition where too much synovial fluid accumulates in the synovial sac. Normal joint fluid acts as a lubricant, reduces friction, and nourishes articular cartilage. However, when the knee joint is inflamed, injured, or affected by a medical condition, the amount of joint fluid increases, causing swelling, pain, and limited movement. This condition affects daily activities, making it difficult to move and work.
The causes of knee effusion are diverse:
- Knee injuries: Sprains, ligament tears, fractures.
- Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis, knee arthritis, knee osteoarthritis.
- Joint diseases: Gout.
- Joint infection.
- Medication use: Side effects of certain drugs.
Symptoms of knee effusion:
- Localized swelling in the knee joint.
- Pain when moving, even at rest.
- Restricted joint movement, difficulty bending, extending, or straightening the leg.
- A feeling of heaviness and tightness in the knee.
- Warmth in the knee joint, possibly accompanied by fever.
Complications and Considerations in Treating Knee Effusion
If left untreated, knee effusion can lead to many complications. Chronic knee arthritis, knee osteoarthritis, and even joint stiffness are potential risks. The knee joint loses flexibility, making daily activities difficult. Prolonged knee conditions affect the quality of life. Joint diseases, musculoskeletal diseases in general, and knee effusion in particular, all require adequate attention.
Rheumatoid arthritis: Prolonged knee effusion increases the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. This condition causes pain, swelling, inflammation, and joint deformity, severely affecting motor function.
Knee osteoarthritis: Synovial fluid lubricates and reduces friction. Prolonged knee effusion causes an imbalance in joint fluid, accelerating the process of knee osteoarthritis. Dry joints and pain during movement are common symptoms.
Joint stiffness: Untreated knee effusion can lead to joint adhesion, restricting movement. Joint stiffness makes daily activities difficult for patients and can result in loss of mobility.
Joint infection: In some cases, knee effusion can be caused by infection. Joint infection is very dangerous and requires immediate treatment to prevent more severe complications.
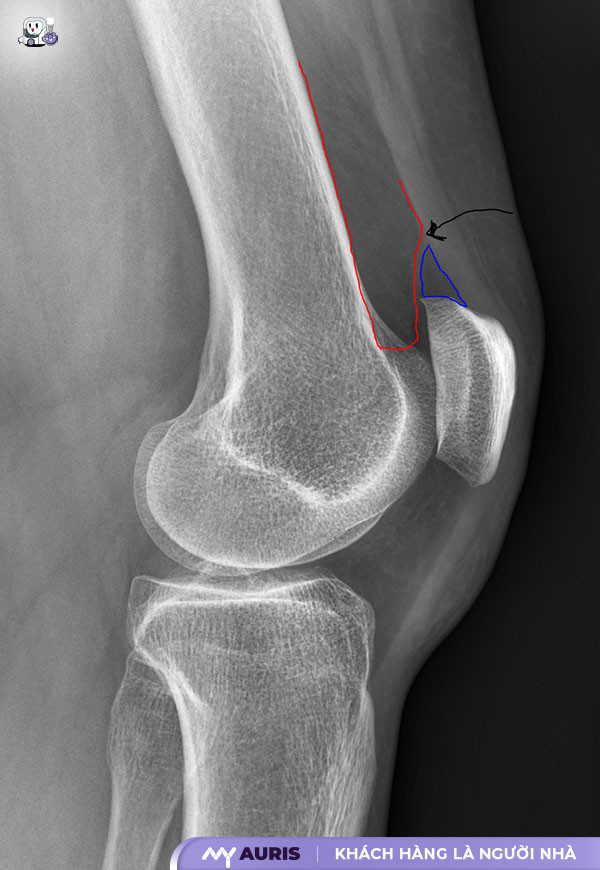
Causes of Knee Effusion
Many factors contribute to knee effusion. Here are some common causes:
Knee injuries: Injuries such as sprains, ligament tears, fractures, or severe impacts can lead to inflammation, swelling, and knee effusion. Knee conditions resulting from trauma require timely treatment to avoid complications.
Rheumatoid arthritis: This is an autoimmune joint disease that causes chronic inflammation in multiple joints, including the knee. Rheumatoid arthritis causes painful knee swelling, restricted movement, and can lead to effusion.
Knee osteoarthritis: The aging process, obesity, or excessive activity can lead to cartilage wear and tear, causing inflammation, pain, and knee effusion. Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition in older adults.
Infectious diseases: Infectious arthritis caused by bacteria or viruses is also a cause of knee effusion. Infectious diseases require immediate medical treatment to prevent spread and complications.
Other medical conditions: Other conditions such as gout, psoriasis, and lupus erythematosus can also cause knee effusion.

Modern Medical Treatments for Knee Effusion
Medical Treatment
Medical treatment is often the first step. Doctors may prescribe pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and swelling in the knee joint. In cases of more severe inflammation, corticosteroids injected directly into the knee joint may be prescribed to quickly reduce inflammation. Note that medication use must follow a doctor’s instructions to avoid side effects.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is often considered when conservative treatments are ineffective. Some common surgical procedures include:
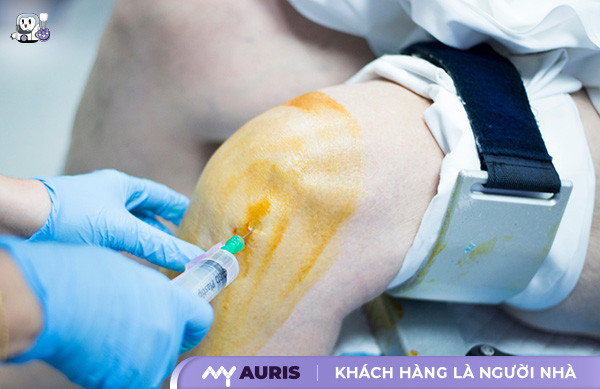
Joint aspiration: This is a simple procedure where a doctor uses a small needle to drain excess fluid from the knee joint, reducing swelling and pain. This method is often combined with corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
Arthroscopy: Doctors use a small arthroscope with a camera to view the inside of the knee joint. During this procedure, they can also repair damaged cartilage or ligaments, or remove inflammatory debris.
Knee replacement: In cases of severe knee osteoarthritis, knee replacement is the ultimate solution to restore function and reduce pain.
Knee Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment and rehabilitation of knee function after effusion. Knee physical therapy exercises help to:
- Strengthen muscles around the knee joint, supporting joint stability.
- Improve range of motion, reducing joint stiffness.
- Reduce pain and swelling.
A physical therapist will guide you through exercises appropriate for your knee condition.
Relieve Pain and Swelling from Knee Effusion at Home with Folk Remedies
Knee pain due to effusion makes daily life difficult. Many people turn to folk remedies to reduce swelling and pain. Here are some methods you can apply:
Hot and Cold Compresses for the Knee Joint
Prepare two towels, one soaked in hot water and one in cold water. Apply the hot towel to the swollen knee joint for about 15 minutes. Next, apply the cold towel for 10 minutes. Repeat this process 3-4 times daily. Hot and cold compresses help reduce pain and swelling in the knee joint. This method is safe and easy to perform at home.

Using Piper sarmentosum (Wild Betel Leaf)
Piper sarmentosum (wild betel leaf) has warming properties that help reduce joint pain. Wash a handful of wild betel leaves, crush them, and apply them to the swollen knee area. Secure with a bandage. Perform this regularly every day for effective knee pain relief.
Ginger and Turmeric
Ginger and turmeric have anti-inflammatory properties. Crush fresh ginger or fresh turmeric, mix with a little salt, and apply to the painful knee area. Leave it on for about 30 minutes, then rinse thoroughly. Repeat twice daily. Note, do not apply if your skin is allergic to ginger or turmeric.
Supportive Diet
Diet plays an important role in treating knee effusion. Supplement your diet with nutrient-rich foods beneficial for joint patients, such as salmon, green vegetables, and fruits. Limit fatty foods, sugar, and stimulants. A scientific anti-inflammatory diet helps boost health, supports the treatment of joint diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, reduces inflammation, and swelling.
Knee Rehabilitation Exercises
Knee physical therapy helps restore joint function, reduce pain, and increase flexibility. Consult your doctor or a physical therapist about knee rehabilitation exercises suitable for your specific knee condition. Physical therapy exercises must be performed correctly to avoid causing further knee injury.
Physical Therapy Exercises for Knee Effusion Rehabilitation
Leg Raises
Lie on your back with your legs straight. Lift the leg with knee effusion about 15-20cm high. Hold this position for 15-20 seconds. Repeat 10-15 times. This exercise helps reduce knee swelling and improves blood circulation. Perform gently, avoiding pain.
Knee Bends and Extensions
Sit on a chair with both feet on the ground. Slowly bend the knee with effusion to a comfortable angle. Hold for 5 seconds, then straighten the leg. Repeat 10-15 times. This exercise helps strengthen muscles and improve knee joint range of motion.
Heel Slides
Lie on your back, bending your healthy knee. Slowly slide the heel of the leg with knee effusion along the floor, extending your leg away. Hold for 5 seconds, then bring the knee back to the starting position. Repeat 10-15 times. This exercise strengthens the quadriceps muscles and supports knee joint stability.
Air Cycling
Lie on your back with your arms by your sides. Lift both legs and perform a cycling motion. Cycle gently for 1-2 minutes. This exercise helps improve blood circulation, reduce swelling, and enhance knee joint flexibility.
Static Exercises
Sit on a chair with both feet on the ground. Contract the quadriceps muscles of the leg with knee effusion for 5-10 seconds, then relax. Repeat 10-15 times. This exercise helps strengthen muscles and supports knee joint stability.

Supportive Diet for Effective Knee Effusion Treatment
Nutrition is the foundation for knee health. A scientific diet helps reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, improve joint flexibility, and support the treatment of knee effusion. Add these foods to your daily diet:
Fatty fish: Salmon, sardines, and tuna are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s help reduce inflammation, alleviate knee pain, and support the treatment of knee effusion, rheumatoid arthritis, knee osteoarthritis, and other joint conditions. Eat fatty fish 2-3 times per week.
Fruits and green vegetables: Supplement with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Vitamin C in oranges and mandarins helps synthesize collagen, strengthening joint cartilage. Fiber in green vegetables helps reduce inflammation. Eat plenty of green vegetables and fruits daily.
Nuts and seeds: Walnuts, almonds, and chia seeds provide omega-3s, fiber, and magnesium. Magnesium helps reduce pain and supports the treatment of knee effusion.
Turmeric: Curcumin in turmeric has powerful anti-inflammatory effects, reducing pain and localized swelling, supporting the treatment of joint effusion, knee arthritis, and knee swelling. Add turmeric to daily meals or use turmeric powder.
Ginger: Ginger has warming properties, helping to reduce pain and swelling, and supporting the treatment of knee effusion. Drink ginger tea or add ginger to your dishes.
Some foods can increase inflammation, making knee effusion more severe. Limit the following foods:
Sugar and processed foods: Sugar increases inflammation and causes joint pain. Limit sweets, soft drinks, and candies.
Red meat: Limit red meat and processed meats as they contain high levels of saturated fat, which can increase inflammation.
Alcoholic beverages: Alcohol increases inflammation and is harmful to joints. Limit or avoid alcoholic beverages.
Distinguishing Symptoms of Knee Effusion from Related Joint Conditions
Knee effusion occurs when too much synovial fluid accumulates, causing swelling in the knee joint. Synovial fluid lubricates and reduces friction. However, when inflamed, injured, or affected by a medical condition, the amount of this fluid increases, leading to pain and limited movement. Common symptoms include localized swelling, pain during movement, restricted joint mobility, a feeling of heaviness in the knee, and warmth in the knee joint.
Distinguishing Knee Effusion from Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis is a chronic condition that progresses slowly, causing pain, dry joints, and stiffness, especially in the morning. Unlike knee effusion, knee osteoarthritis is common in older adults, resulting from cartilage wear and tear. The condition is often accompanied by creaking or popping sounds during movement.
Distinguishing Knee Effusion from Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune inflammatory disease that affects multiple joints, often symmetrically. It causes pain, swelling, and joint stiffness, especially in the morning. Systemic symptoms such as fatigue and low-grade fever may also occur. Unlike knee effusion, rheumatoid arthritis is often accompanied by systemic inflammatory symptoms.
Distinguishing Knee Effusion from Knee Injury
Knee injuries, such as sprains and ligament tears, also cause pain, swelling, and effusion. However, injuries usually occur suddenly after an impact or fall. Differentiation can be made by reviewing the history of trauma.
Distinguishing Knee Effusion from Knee Ligament Pain
Knee ligament pain is often caused by overuse or injury. Symptoms include localized pain in the affected ligament area, possibly accompanied by mild swelling. Unlike knee effusion, knee ligament pain does not cause prominent swelling as seen in knee effusion.