Periodontal disease is a common oral disease, however many people are subjective and do not treat it early. Furthermore, many people confuse it with gingivitis. Periodontal disease causes many effects on oral health, even permanent tooth loss if not treated promptly. Sowhat is periodontal disease? Join My Auris to learn more about this disease in the following article.
What is periodontal disease?
The periodontium is the organization surrounding the tooth that is responsible for supporting and storing the tooth root in the bone. The reason why teeth are healthy and kept in the jawbone is thanks to the ligaments, gums and alveolar bone. The part of the gum that hugs the teeth protects the sensitive tissue underneath from bacteria entering and causing harm.
Periodontal disease is a periodontal infection that directly affects the tissues that support teeth. From there, the teeth lose their connection to these supporting organizations. Bacteria initially enter the periodontal pocket, causing the gums to recede, exposing the tooth roots. Over time, the infection becomes more and more serious and the gum tissue will be damaged, teeth will loosen, teeth will be lost and the alveolar bone will be affected.
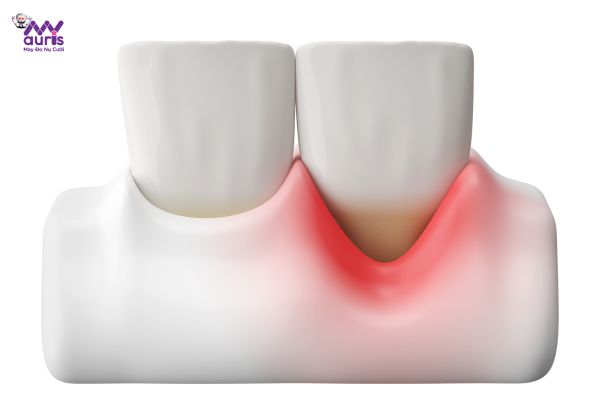
Although periodontal disease is a common oral disease, many people often subjectively let the condition persist and progress without early intervention and treatment. Once treatment begins, the disease is severe and difficult to control, causing teeth to weaken and leading to complete tooth loss.
Causes of periodontal disease
The main cause of periodontitis is poor oral hygiene, causing more and more plaque to accumulate on the teeth. Dental plaque is a hard biofilm that contains many harmful bacteria, causing many inflammatory diseases for oral health. If this plaque is not removed periodically, it will gradually calcify into tartar, causing the gums to become seriously inflamed and then turn into periodontitis.
Besides plaque and tartar as the main causes, a number of risk factors also increase periodontitis:
- Hormonal changes cause sensitive gums, increasing the risk of periodontitis
- Some diseases: cancer, immunodeficiency, diabetes,… increase the risk of infection, especially periodontitis
- Smoking
- Side effects of some medications
- Family history of dental disease.
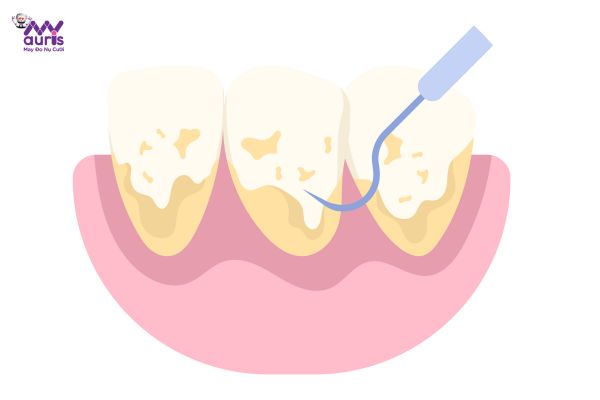
When understanding the cause of the disease, people will know how to practice better oral hygiene and get regular dental cleanings for prevention. Besides, it is also necessary to change your lifestyle and healthy living regimen to both improve your body’s health and improve your oral health.
Signs of periodontal disease
The disease has similar signs to other oral diseases, so sometimes it causes confusion. However, as soon as you detect problems with your oral health and the following signs appear, you should go to the doctor for examination and examination as soon as possible: >
- Red, swollen gums, often bleeding, most commonly when brushing teeth
- Bad breath.
- Use your hand to press the gums and see pus coming out.
- Unusual feeling when chewing food
- Teeth are most sensitive when exposed to hot or cold foods
- Teeth are loose and increasingly spaced.
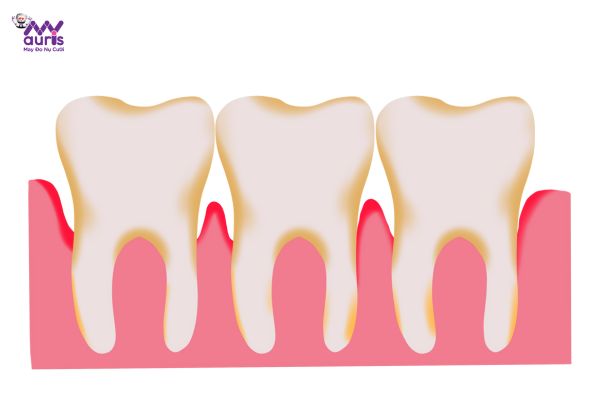
The disease will be divided into 2 stages: gingivitis and periodontitis. In the gingivitis stage, it is easier to treat and control than periodontitis. As the disease progresses, periodontitis causes bacteria to penetrate deeply beneath the gums, such as bone and periodontal ligament, causing a high risk of permanent tooth loss.
How to treat periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease, if not treated promptly, will cause complete tooth loss. Next, the bacteria diecontinues to penetrate deep into other organizations, affecting the body’s health. Therefore, as soon as symptoms appear, patients should see a dentist as soon as possible.
Depending on the severity of the disease, doctors recommend different treatment methods:
Emergency treatment cases
- In cases of mucosal or gingival abscesses, emergency treatment will be indicated.
- Cases with signs of red, swollen mucosa, severe pain, and palpable heaving. The pus can be temporarily cured when the patient self-administers anti-inflammatory antibiotics, but the disease still exists and enters a chronic state, then still flares up acutely, recurs cyclically and becomes increasingly serious.
Non-surgical treatment
- Correct or replace all improper fillings and restorations.
- Evaluate and specify the teeth that need to be extracted. These teeth cannot be kept.
- Fix teeth if there are loose teeth.
- Perform a temporary restoration if necessary
- Scraping tartar and treating tooth base surface
- Dip your teeth with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
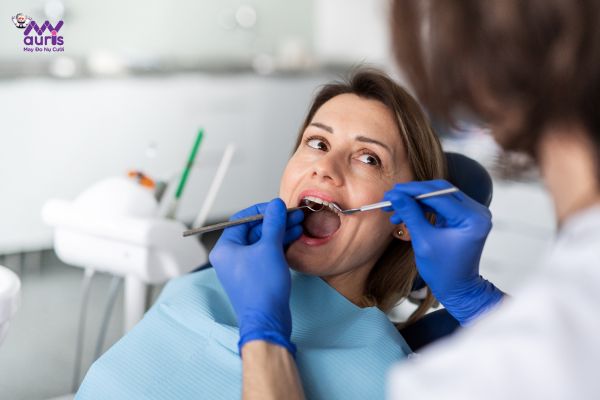
Surgical treatment
Surgery is only applied when conventional measures do not bring results result:
- Surgical removal of periodontal pockets: reduces the depth of periodontal pockets, facilitates hygiene, cleans plaque and bacteria on teeth.
- Regenerative surgery: bone and periodontal tissue are destroyed, forming periodontal pockets around the teeth. These pockets become deeper and contain more bacteria, affecting bone and periodontal tissue. This causes the teeth to loosen a lot. After surgery, some bone and periodontal tissue can regenerate.
- Soft tissue graft surgery: gum recession causes tooth roots to be exposed. This surgical method will restore damage and prevent gum recessioncontinues to happen. Surgery can be performed on one or more teeth to bring harmony to the gum line and improve tooth sensitivity and sensitivity.
Maintenance treatment
After applying treatment methods and the disease has stabilized, the patient needs to be monitored, examined periodically and comply with maintenance treatment measures to control symptoms and prevent disease recurrence.
Prevention of periodontal disease
As mentioned, understanding the cause of the disease will help people find effective ways to prevent the disease:
- Proper and careful oral hygiene: brush your teeth at least twice a day, morning and evening. Brush your teeth properly and with the right technique to avoid using too much force or using a large toothbrush with hard bristles that can damage your gums. Brush your teeth thoroughly to remove plaque, food particles, and bacteria.
- Combining the use of dental floss, mouthwash and salt water to increase the effectiveness of cleaning the oral cavity, killing bacteria, and removing food particles and plaque in places where the bristles cannot reach.
- Dental examination, regular tooth scaling
- Avoid smoking
- If there is a systemic disease, the patient should monitor their health and treat the disease according to the doctor’s regimen to control symptoms and progression affecting oral health.

Hopefully the information in the article aboutwhat is periodontal disease will help people better understand this disease. From there, know how to care for and protect oral health to prevent dangerous diseases and complications from occurring. If you are still worried, please contact My Auris dentistry immediately for more detailed advice and answers.
Anh Thy





